powershell
-
Go to your media library and switch to the ‘List View’
-
Then under ‘Screen Options’ bump up the ‘Number of items per page’ to a big number
-
Right click to ‘View Page Source, then save it somewhere on your computer
-
Run the following in PowerShell
-
Go to your media library and switch to the ‘List View’
-
Then under ‘Screen Options’ bump up the ‘Number of items per page’ to a big number
-
Right click to ‘View Page Source, then save it somewhere on your computer
-
Run the following in PowerShell
- I'd really rather not do this, but I can't find a safe and seen-to-be-safe way of doing what I want to do through PowerShell or any other automated tool ↩
-
The ‘better way’ is to use
gci -force. That includes all the system databases. ↩︎ - one should test one’s code
- if you put something invalid in a ‘select’ list in Powershell it won’t necessarily error
list AD users in powershell
This shows all the users with ‘dba’ in their username. Obviously you could leave out the filter clause altogether to get a complete list of AD users
Get-ADUser -Filter {samaccountname -like "*dba*"} -SearchBase "dc=mycomp,dc=co,dc=uk" |
select samaccountname, name
samaccountname name
-------------- ----
dba_john John Hollins
dba_terry Terry Dixon
You have to ActiveDirectory Powershell module loaded
how to get a list of images uploaded to wordpress.com website
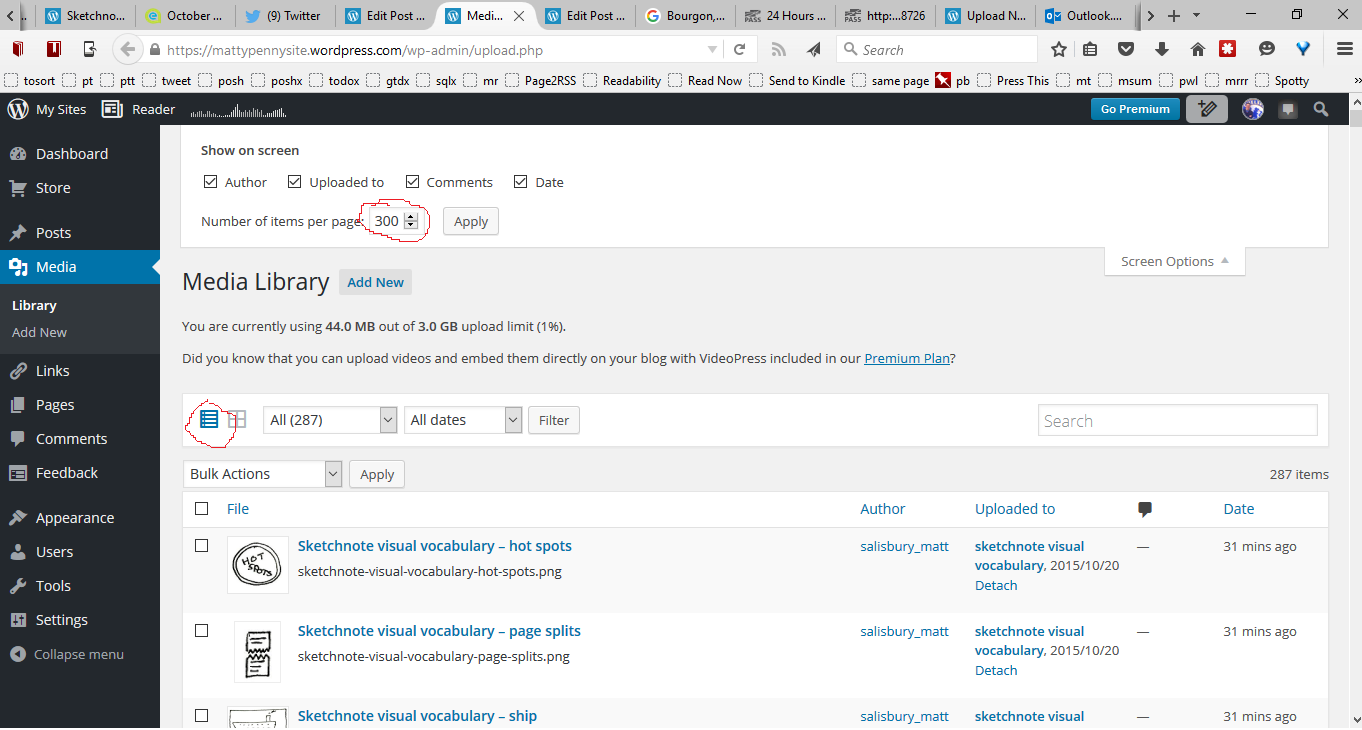
foreach ($line in select-string filename .\upload.php | Sort-Object -Property line ) {
$line.line.split(">")[3].split("<")[0]
}
This gives you a list that looks like this:
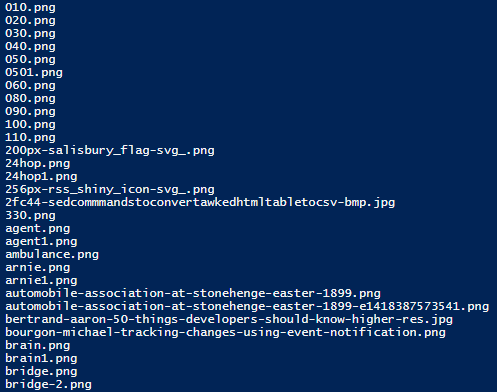
how to get a list of images uploaded to wordpress.com website

foreach ($line in select-string filename .\upload.php | Sort-Object -Property line ) {
$line.line.split(">")[3].split("<")[0]
}
This gives you a list that looks like this:

Powershell function to get Sqlserver errorlog recent lines
I’ve started knocking up a function to return the last few lines of a sqlserver errorlog.
This is a little way from being finished….but I’ve already found it quite handy
function get-sqlerrorlog {
[CmdletBinding()]
Param(
[String] [alias("computer")] $ComputerName,
[Int] [alias("lines")] $NumberOfLines = 5
)
write-verbose "Running function $([string]$MyInvocation.MyCommand.name)"
Write-verbose "`$ErrorLogFolder: $ErrorLogFolder"
$ErrorLogFolder = dir sqlserver:\sql\$ComputerName
# Todo: need to work out how it works more > 1 named instance. This just picks 1st
[string]$ErrorLogFolder = $($ErrorLogFolder | select -first 1).errorlogpath
Write-verbose "`$ErrorLogFolder: $ErrorLogFolder"
$ErrorLogFolder = $ErrorLogFolder.replace(':', '$')
Write-verbose "`$ErrorLogFolder: $ErrorLogFolder"
$ErrorLogFolder = '\\' + $ComputerName + '\' + $ErrorLogFolder
Write-verbose "`$ErrorLogFolder: $ErrorLogFolder"
# Todo: it might be that the get-content could be speeded up by retrieving less lines
# Todo: seperate this bit out into seperate function ?
get-content "$ErrorLogFolder\ERRORLOG" | select -last $NumberOfLines
}
set-alias gsel get-sqlerrorlog
getting a list of aliases ordered by the aliasee
This is fairly trivial…and I’ve no idea if ‘aliasee’ is a real word or not, but I found this quite useful today:
get-alias | select ResolvedCommand, name | sort -property resolvedcommand
On my laptop, this gives:
ResolvedCommand Name
--------------- ----
Add-Content ac
Add-PSSnapin asnp
Clear-Content clc
Clear-History clhy
Clear-Host cls
Clear-Host clear
Clear-Item cli
Clear-ItemProperty clp
Clear-Variable clv
Compare-Object diff
Compare-Object compare
Connect-PSSession cnsn
Convert-Path cvpa
Copy-Item cp
Copy-Item copy
Copy-Item cpi
Copy-ItemProperty cpp
Disable-PSBreakpoint dbp
Disconnect-PSSession dnsn
Enable-PSBreakpoint ebp
Enter-PSSession etsn
Exit-PSSession exsn
Export-Alias epal
Export-Csv epcsv
Export-PSSession epsn
ForEach-Object foreach
ForEach-Object %
Format-Custom fc
Format-List fl
Format-Table ft
Format-Wide fw
Get-Alias gal
get-cal cal
Get-ChildItem dir
Get-ChildItem ls
Get-ChildItem gci
Get-Command gcm
Get-Content cat
Get-Content gc
Get-Content type
get-functions getf
Get-History history
Get-History ghy
Get-History h
Get-Item gi
Get-ItemProperty gp
Get-Job gjb
Get-Location pwd
Get-Location gl
Get-Member gm
Get-Module gmo
get-os gos
Get-Process gps
Get-Process ps
Get-PSBreakpoint gbp
Get-PSCallStack gcs
Get-PSDrive gdr
Get-PSSession gsn
Get-PSSnapin gsnp
Get-Service gsv
Get-Unique gu
Get-Variable gv
Get-WmiObject gwmi
Group-Object group
help man
Import-Alias ipal
Import-Csv ipcsv
Import-Module ipmo
Import-PSSession ipsn
Invoke-Command icm
Invoke-Expression iex
Invoke-History r
Invoke-History ihy
Invoke-Item ii
Invoke-Locate.ps1 locate
Invoke-NullCoalescing ??
Invoke-RestMethod irm
Invoke-WebRequest wget
Invoke-WebRequest iwr
Invoke-WebRequest curl
Invoke-WmiMethod iwmi
Measure-Object measure
mkdir md
Move-Item move
Move-Item mv
Move-Item mi
Move-ItemProperty mp
New-Alias nal
New-Item ni
New-Module nmo
New-PSDrive mount
New-PSDrive ndr
New-PSSession nsn
New-PSSessionConfigurationFile npssc
New-Variable nv
Out-GridView ogv
Out-Host oh
Out-Printer lp
Pop-Location popd
powershell_ise.exe ise
Push-Location pushd
Receive-Job rcjb
Receive-PSSession rcsn
Remove-Item rmdir
Remove-Item del
Remove-Item rd
Remove-Item rm
Remove-Item erase
Remove-Item ri
Remove-ItemProperty rp
Remove-Job rjb
Remove-Module rmo
Remove-PSBreakpoint rbp
Remove-PSDrive rdr
Remove-PSSession rsn
Remove-PSSnapin rsnp
Remove-Variable rv
Remove-WmiObject rwmi
Rename-Item rni
Rename-Item ren
Rename-ItemProperty rnp
Resolve-Path rvpa
Resume-Job rujb
Select-Object select
Select-String sls
Set-Alias sal
Set-Content sc
set-debug db
Set-Item si
Set-ItemProperty sp
Set-Location sl
Set-Location chdir
Set-Location cd
Set-PSBreakpoint sbp
Set-Variable sv
Set-Variable set
Set-WmiInstance swmi
Sort-Object sort
Start-Job sajb
Start-Process start
Start-Process saps
Start-Service sasv
Start-Sleep sleep
Stop-Job spjb
Stop-Process kill
Stop-Process spps
Stop-Service spsv
Suspend-Job sujb
Tee-Object tee
Trace-Command trcm
Update-LocateDB.ps1 updatedb
Wait-Job wjb
Where-Object where
Where-Object ?
Write-Output write
Write-Output echo
how to rdp to several desktops one after the other
For reasons that aren’t necessarily relevant, I wanted to use Remote Desktop to visit a list of servers1. I tried doing this:
foreach ($S in "server01", "server02, "server03") {
mstsc /f /V:$S
}
This works….but it immediately starts rdp sessions to each of the servers. This is fine in this example, where there are only 3 servers, but in real life I’ve got a list of twenty or so and I don’t really want to open 20-odd rdp sessions at once.
What I did instead to force it do the rdp’s sequentially was this:
foreach ($S in "server01", "server02, "server03") {
mstsc /f /V:$S
$ThrowAway = read-host "Hit Return"
}
how to extract tweets about...
This was the Powershell code I used to create the all the podcasts I’ve ever tweeted about post.
I downloaded the tweets from Twitter itself - I think there was a link somewhere within ‘Settings’
The .csv file looks like this:

So the code is:
$PodTweets = Import-Csv c:temptweets.csv | ? text -like "*podcast*"
$TweetsAsHtml = foreach ($P in $PodTweets)
{
# write-output $P.timestamp.Substring(0,10)
# Splitting the tweet text into words to allow for the processing of urls
$TweetTextAsArray = $P.text.split(" ")
$TextWithLink=""
foreach ($Word in $TweetTextAsArray)
{
if ($Word -like "http:*")
{
# if there is an expanded_url, then use that instead
if ($P.expanded_urls -ne "")
{
$Word = $P.expanded_urls
# for some reason the expanded url is sometimes repeated in the download
if ($Word -like "*,*")
{
$Word = $Word.split(",")[0]
}
}
# re-format the URL as a link
$Word = "`<a href=`"$Word`"`>$Word`<`/a`>"
}
$TextWithLink = "$TextWithLink$Word "
}
# create an object and output that
$properties = @{'TweetDate'=$P.timestamp.Substring(0,10);
'TweetText'=$TextWithLink}
$ReformattedTweets = New-Object -Type PSObject -Prop $properties
write-output $ReformattedTweets
}
$TweetsAsHtml | fl | out-file -encoding ascii -FilePath x.txt -width 1000
system databases not included in powershell sqlserver provider 'databases' folder
I hadn’t noticed this before.
If you do a dir listing of the databases for an instance within the Powershell Sqlserver provider, it doesn’t show the system databases
PS C:powershell> dir SQLSERVER:\SQL\my_pcinst2012\databases
Name Status Recovery Model CompatLvl Collation Owner
---- ------ -------------- --------- --------- -----
AdventureWorks2012 Normal Simple 110 SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS matty
TSQL2012 Normal Full 110 Latin1_General_CI_AS matty
To get a listing for the system databases you can do the following. I would imagine there’s a better way (perhaps some equivalent to ls -a?)…but I can’t think of it at the minute1
PS C:powershell> foreach ($DB in ("master", "msdb", "model", "tempdb")) {gi SQLSERVER:\SQL\my_pcinst2012\databases\$DB }
Name Status Recovery Model CompatLvl Collation Owner
---- ------ -------------- --------- --------- -----
master Normal Simple 110 Latin1_General_CI_AS sa
msdb Normal Simple 110 Latin1_General_CI_AS sa
model Normal Simple 110 Latin1_General_CI_AS sa
tempdb Normal Simple 110 Latin1_General_CI_AS sa
Powershell pattern matching to check if a string is hex
 I’ve been playing with pattern matching in Powershell.
I’ve been playing with pattern matching in Powershell.
I was trying to use ‘-match’ to ‘Check if the string is a hexadecimal number’ for the ‘Perl one-liners in Powershell’ page I’ve been working on.
I can’t pretend to entirely understand or explain pattern matching in Powershell, or in linux, but this seems to work.
$X = "21e" ; $Y = $X.length ; $X -match "[0123456789abcde]{$Y}"
This says match the string against ‘any combination of the characters within the square brackets (i.e. the hex digits) to the same length as the original string’.
So, the square brackets contain the allowable characters.
The curly brackets give the number of characters.
I tried just doing:
$X = "21e" ; $X -match "[0123456789abcde]{$X.length}"
…but this didn’t seem to work.
Tests
I tried the following strings - they all seemed to come up with the right answer: ``` $ $X = "21e" ; $Y = $X.length ; $X -match "[0123456789abcde]{$Y}" True $ $X = "21edjhsd" ; $Y = $X.length ; $X -match "[0123456789abcde]{$Y}" False $ $X = "21e34782348237847832748723" ; $Y = $X.length ; $X -match "[0123456789abcde]{$Y}" True $ $X = "21e34782348237847832748723f" ; $Y = $X.length ; $X -match "[0123456789abcde]{$Y}" False $ $X = "21e34782348237847832748723acbdaaa" ; $Y = $X.length ; $X -match "[0123456789abcde]{$Y}" True $ $X = " " ; $Y = $X.length ; $X -match "[0123456789abcde]{$Y}" False ```….although I’m not sure whether this is right or wrong:
$ $X = "" ; $Y = $X.length ; $X -match "[0123456789abcde]{$Y}"
True
Mis-spelling in Powershell
This was spectacularly incompetent even by my high standards of incompetence.
It illustrates that if you spell the name of a column incorrectly in Powershell, you don’t get an error, you just get a null column
get-wmiobject -class win32_operatingsystem -computer rdm016 |
select __Server, ServicePackMajorVerstion
And got:
__SERVER ServicePackMajorVerstion
-------- ------------------------
RDM016
I thought that no service packs had been applied. This, as more attentive readers will have spotted, was not the case. The null under ServicePackMajorVerstion is because you don’t spell ‘version’ with a ’t'. Two learnings from this:
How to report mp3 tags in Powershell
I’m slowly getting to grips with Powershell.
# -----------------------------------------------------------------
# Script - Catalog-MP3s.ps1 #
# Gets mp3 tags from the mp3 file.
# -----------------------------------------------------------------
# Parameter is either a directory or an individual mp3 Param ( $P_DIR_OR_MP3 )
# --------------------------
# Function: get-mp3info
# The function gets the tags
# for the specified mp3
# --------------------------
Function get-mp3info ($P_MP3)
{
# Get the tages into a variable
$TAGS = [TagLib.File]::Create("$P_MP3")
$TAGS_OBJECT = @{Filename = $TAGS.Name;
Bitrate = $TAGS.Properties.AudioBitRate;
Artist = $TAGS.tag.FirstArtist;
Title = $TAGS.tag.Title;
Genre = $TAGS.tag.FirstGenre;
LP = $TAGS.tag.Album}
# Output as an object
New-Object PSObject -Property $TAGS_OBJECT
}
# --------------------------
# Main body
# --------------------------
# Store the location of the taglib dll
$TAGLIB="C:\Users\Matt\Downloads\taglib-sharp-2.1.0.0-windows\taglib-sharp-2.1.0.0-windows\Libraries\tag\lib-sharp.dll"
# Load the DLL
[System.Reflection.Assembly]::LoadFile($Taglib)
# Get a list of all the MP3s under the specified folder
# - exclude anything that's not an mp3
# - Fullname contains the full path and filename
$MP3_LIST = gci -recurse Filesystem::$DIR_OR_MP3 |
where {$_.Extension -eq '.mp3'} |
select FullName
# Walk through the list, and output the tags
foreach ($MP3 in $MP3_LIST)
{
get-mp3info $MP3.Fullname
}
The heavily borrows from: